IV-related falls are a major safety concern in hospitals, affecting up to 1 million patients annually and costing billions in healthcare expenses. This guide outlines five simple, actionable steps to minimize these risks and improve patient safety:
- Organize IV Lines: Use tools like the Beata Clasp® to prevent tangling and keep lines off the floor.
- Secure IVs and Tubing: Properly anchor catheters and route tubing to avoid dislodgement during movement.
- Train Staff on Safety: Provide hands-on training for IV management, fall prevention, and safe patient mobility.
- Help Patients Move Safely: Use pre-movement assessments, mobility aids, and clear communication to reduce fall risks.
- Check for Safety Risks: Conduct daily inspections of IV lines, equipment, and patient areas to address hazards.
How to Avoid Falls in the Hospital
Step 1: Keep IV Lines Organized
Organizing IV lines properly is crucial for patient safety and mobility. Research shows that over 60% of line, tube, and drain incidents in ICUs can be avoided with proper organization.
Using the Beata Clasp System
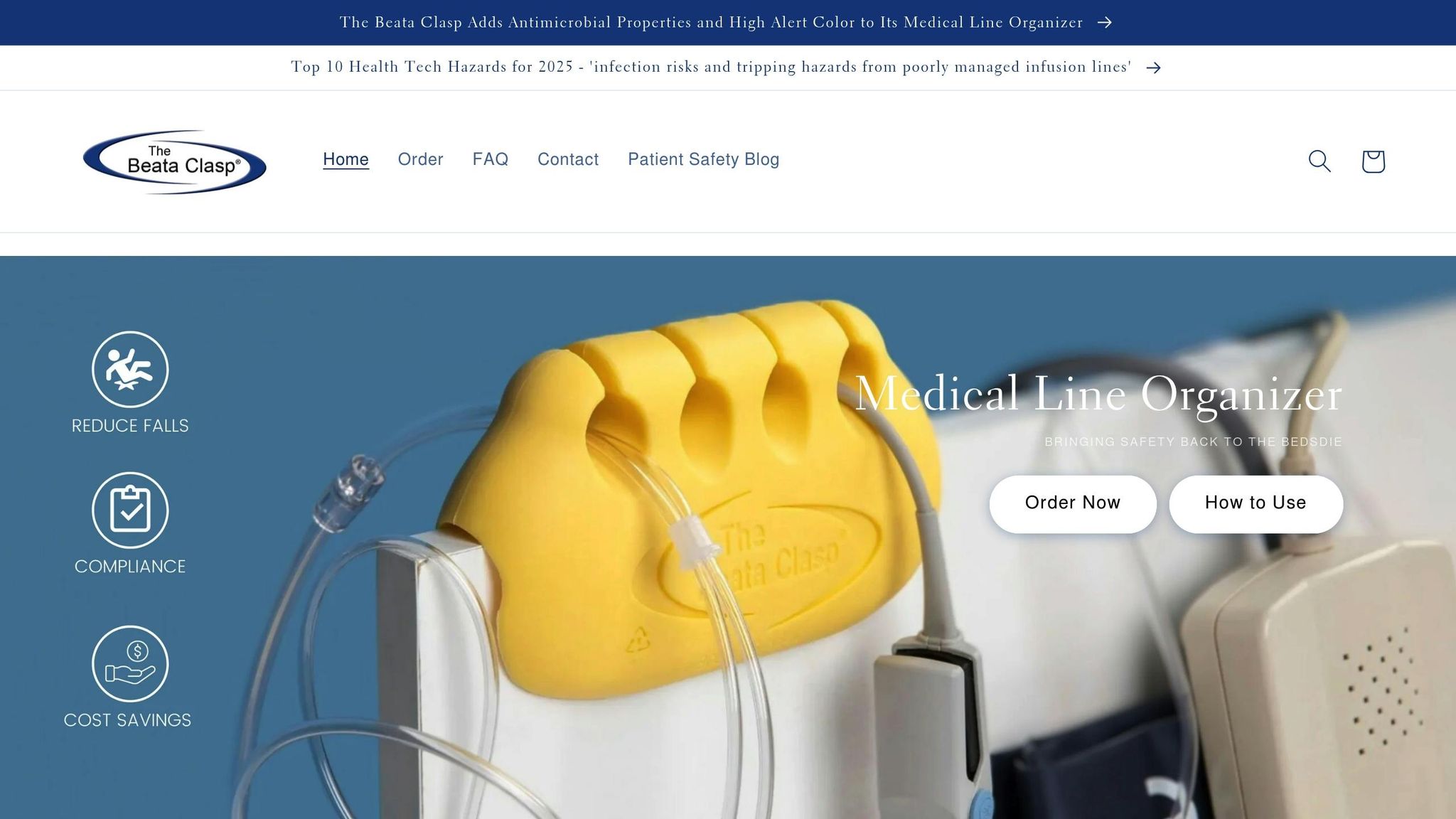
The Beata Clasp® is a practical tool for managing multiple IV lines. This device attaches securely to bedrails, IV poles, or wheelchairs, keeping lines neatly separated and off the floor. Its circular grooves prevent tangling and reduce tripping hazards.
Here’s how the Beata Clasp® helps prevent falls:
| Feature | How It Enhances Safety |
|---|---|
| Line Separation | Avoids tangling, making line tracing easier |
| Floor Clearance | Keeps tubes off the floor, reducing tripping risks |
| Secure Attachment | Maintains organization during patient movement |
| Easy Tracing | Simplifies identifying and following lines to their source |
"This study indicates that nurses had favorable impressions of the Beata Clasp®, a product specifically developed to address the confusion and disorder generated by multiple tubes and lines. The majority of nurses judged the Beata Clasp® effective in reducing the 'spaghetti syndrome,' and believed it had a beneficial impact on patient safety and nursing efficiency." - BeataClasp.com
For even better results, combine this tool with clear and consistent line management protocols.
Line Management Guidelines
Adhering to line management protocols is another key step in minimizing risks. A study in ICUs found that 56% of patients with line-related incidents suffered physical injuries, and 23% required longer hospital stays.
- Initial Setup: Always trace lines back to their source before connecting or disconnecting. This ensures proper identification and avoids misconnections.
- Ongoing Management: Regularly check line organization during each shift. Remove unnecessary extensions and consolidate lines to avoid tangling.
- Transport Preparation: Since 45% of transport-related issues involve line complications, secure and organize all lines before moving a patient.
Facilities that prioritize tools like the Beata Clasp® and enforce strong line management protocols report fewer falls, improved patient safety, and reduced healthcare costs. Proper training and the right tools make a measurable difference in outcomes.
Step 2: Secure IVs and Tubing
Properly securing IVs and tubing is crucial to minimize accidental dislodgment and reduce fall risks. Without securement, IV dislodgment happens in up to 42% of cases.
IV Catheter Anchoring
Stabilizing catheters effectively can prevent complications that might lead to falls. Different securement methods offer various benefits:
| Securement Method | Safety Benefit | Impact on Falls |
|---|---|---|
| Sutureless Securement | Reduces IV complications by up to 67% | Limits unexpected line movement |
| Commercial Stabilization | Cuts unscheduled catheter restarts by about 49% | Decreases sudden disconnections |
| Under/Over Taping | Provides strong resistance against applied forces | Helps prevent dislodgment during movement |
Commercial stabilization devices, which are sterile and latex-free, not only eliminate the need for sutures but also improve patient comfort. These systems keep IV lines securely anchored, even when the patient is moving.
Strategically placing IV lines is another key step in reducing fall risks.
IV Line Placement
Thoughtful IV line placement enhances mobility and reduces hazards. Here are two practical strategies to consider:
- Secure Line Routing: Keep IV lines elevated and away from high-traffic areas to avoid floor contact.
- Equipment Integration: Attach IV lines to bed rails or wheelchairs and ensure call bells are easily reachable.
Following a structured approach to line management not only improves care delivery but also significantly lowers the risk of falls. Regularly checking the securement methods ensures their effectiveness, and many healthcare facilities have seen improved patient safety by consistently applying these practices.
sbb-itb-f779e18
Step 3: Train Staff on Safety
Proper training for staff plays a critical role in reducing IV-related falls by ensuring consistent safety measures during patient care.
Staff Training Topics
Training programs should center on safety practices that directly reduce fall risks. Combining theoretical instruction with hands-on practice makes the training more effective.
| Training Component | Key Focus Areas | Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Core Safety Protocols | IV line management, patient assessment | Regular hands-on demonstrations |
| Fall Prevention Methods | Universal precautions, risk screening | Scenario-based learning |
| Mobility Assistance | Safe transfer and equipment use | Practice with mobility aids |
| Documentation | Risk assessment, incident reporting | Electronic health record training |
"Fall prevention should be a multi-disciplinary effort including physicians, physical and occupational therapists, patients and their families, and of course, nurses." - Performance Health
Maintaining Safety Standards
Building a supportive unit culture helps maintain consistent safety practices. Healthcare facilities can reinforce these protocols through several strategies:
-
Regular Assessment Reviews
Staff should routinely complete patient fall risk screenings, document findings, and ensure necessary mobility aids are available based on patient needs. -
Clear Communication Systems
Establish clear handoff protocols so all team members stay informed about current fall prevention strategies. This includes documenting patient-specific precautions and discussing updates during shift changes. -
Encouraging a Learning Environment
Promote a non-punitive safety reporting system that focuses on learning from incidents. This approach strengthens the safety culture and improves risk management efforts.
These steps help keep safety practices adaptable and responsive, paving the way for more effective patient mobility strategies.
The Safe Recovery Program is a good example of how training can make a difference. By focusing on individualized patient education and tailored follow-up protocols, many healthcare facilities have improved teamwork and created a stronger safety culture around fall prevention.
Key training reminders include:
- Monitoring medication side effects that may increase fall risks
- Keeping floors clean, dry, and well-lit
- Ensuring patients have access to proper non-slip footwear
- Following facility-specific patient assistance protocols
Regular refresher courses help staff stay updated on the latest best practices for preventing IV-related falls. A well-prepared team is essential for safely managing patient mobility, which we’ll cover in the next step.
Step 4: Help Patients Move Safely
Ensuring patients can move safely with IV lines requires careful coordination. By combining proper preparation and secure equipment, you can reduce the risk of falls and injuries.
Walking with IV Lines
Helping a patient walk with IV lines takes planning and clear communication. Falls in healthcare settings can lead to serious injuries, making safe movement protocols essential.
Here’s what to focus on:
- Pre-Movement Assessment: Before helping a patient move, check for any medication side effects, ensure they’re wearing proper footwear, confirm the IV is secure, and assess their alertness.
-
Movement Support Tips:
- Stand on the patient’s weaker side to provide better support.
- Use a gait belt to assist during movement.
- Keep IV lines organized and untangled.
- Clearly communicate each step of the process to the patient.
Using the right mobility aid can further enhance safety during these movements.
Choosing Movement Aids
Pairing safe walking techniques with the right equipment can make a big difference. Falls are a common issue in healthcare settings, with up to 75% of nursing home residents experiencing them each year. This makes selecting the right mobility aid critical.
| Movement Aid Type | Benefits | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Modified Walkers | Helps patients manage IVs alone | Those undergoing long-term IV therapy |
| Personal IV Poles | Allows hands-free movement | Patients with good balance |
| Transfer Belts | Offers extra staff support | Early mobility sessions |
| Bathroom Support Rails | Improves stability during transfers | Personal care activities |
Key safety tips:
- Always keep mobility aids within easy reach.
- Make sure IV lines are visible and not tangled.
- Regularly inspect equipment for stability and proper function.
- Position call bells so patients can easily access them.
Providing a variety of reliable mobility aids ensures that patient needs are met effectively.
Step 5: Check for Safety Risks
Regular inspections are crucial to identifying and addressing IV-related hazards, ensuring patient safety.
Safety Checklist
Using a checklist helps identify potential issues effectively. According to recent reports, "infection risks and tripping hazards from poorly managed infusion lines" rank among the top 10 Health Tech Hazards for 2025.
Here are the key areas to focus on during safety rounds:
| Inspection Area | Check Points | Required Action |
|---|---|---|
| IV Lines | Tangles, kinks, proper routing | Reorganize using line management tools |
| Equipment Placement | IV pole stability, proper height | Adjust and secure equipment |
| Floor Space | Clear pathways, proper cord management | Remove obstacles and secure loose items |
| Bed Setup | Rail position and line clearance | Adjust rails and verify line organization |
| Patient Area | Accessibility of call bell and mobility aids | Ensure items are within easy reach |
Daily checks should confirm:
- IV lines are properly organized and functioning.
- All IV catheters are securely anchored.
- Pathways around patient beds are clear and free of hazards.
These daily inspections form the foundation for maintaining a safe environment and help avoid preventable incidents.
Regular Safety Reviews
Regular reviews are essential for maintaining safety standards. For example, hospitals have reported increased risks when beds with four bedrails caused IV lines to tangle or fall as the bed's head was raised.
Review Schedule:
- At shift changes.
- During periodic spot checks.
- Through a full review each day.
- Document all findings and actions taken.
Keeping IV lines separated minimizes the chance of accidental dislodgement, which could lead to bleeding, injury, or loss of IV access.
Detailed documentation of safety reviews not only ensures compliance but also helps identify recurring issues. This proactive approach supports better prevention strategies and reduces IV-related risks in clinical settings.
Conclusion: Putting Safety Steps into Practice
Key Steps for Prevention
Preventing IV-related falls involves a structured five-step plan:
| Step | Focus Area | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Line Organization | Proper routing and management | Minimizes tangling and tripping hazards |
| Secure Placement | Anchoring IV catheter and tubing | Reduces accidental dislodgement |
| Staff Training | Safety protocols and procedures | Promotes consistent prevention efforts |
| Patient Mobility | Safe movement techniques | Lowers fall risks during transfers |
| Safety Monitoring | Regular inspections and reviews | Upholds safety standards over time |
This approach not only prioritizes patient safety but also helps reduce financial burdens.
Results of Safety Programs
Applying these steps consistently leads to safer environments and fewer financial risks for healthcare facilities. Preventing falls reduces costs tied to injuries, which can be a heavy financial strain.
For context, fall-related medical costs were $30 billion in 2010, climbing to an estimated $54.9 billion annually by 2020. By adopting these measures, facilities can lower treatment expenses, avoid reimbursement losses, and create a safer experience for patients.
Customizing these strategies to fit specific units ensures the best results. Combining effective line management tools, regular training, and ongoing safety checks forms a well-rounded plan that addresses various risks at once.
