The LMAP Framework by WorldMed is a structured system for safer IV line management in healthcare settings. It standardizes procedures to reduce errors, like infections or misconnections, ensuring consistent practices across teams. The framework focuses on four key areas:
- Leadership & Policy: Clear protocols for IV line handling.
- Monitoring Systems: Audits and metrics to identify safety gaps.
- Standardized Tools: Consistent workflows and tools like the Beata Clasp for organization.
- Staff Training: Continuous education to ensure protocol adherence.
How To Maintain An IV Line? - Nursing Knowledge Exchange
4 Core Components of the LMAP Framework
The LMAP Framework is built on four interconnected components that work together to establish a reliable safety system. These elements focus on key aspects of IV line management, ensuring healthcare facilities can maintain safe and consistent practices across all departments and shifts.
Leadership and Policy Development
Leadership plays a critical role in setting clear IV line policies. These policies cover everything from identification and maintenance to handling emergencies, ensuring consistent procedures are in place.
But leadership isn’t just about creating policies - it’s also about providing the resources needed for safety initiatives, supporting staff training, and holding teams accountable for following protocols. Strong leadership fosters a workplace culture where IV line safety is a priority.
Policies should address real-world scenarios healthcare workers face daily. For instance, they should include guidelines for managing patients with multiple IV lines, handling line changes during shift transitions, and responding to potential complications. These detailed protocols remove uncertainty and help ensure consistent care.
Monitoring and Assessment Systems
Regular audits are essential for identifying gaps between established protocols and how they’re actually implemented. Using audits, metrics, and feedback loops, healthcare facilities can evaluate the effectiveness of their IV line management practices. This ongoing monitoring helps uncover hidden risks and ensures practices align with safety standards.
For example, The Joint Commission mandates that hospitals use evidence-based strategies to continuously monitor infection rates, aiming to reduce hospital-acquired infections. The data collected from these assessments provides actionable insights, allowing facilities to focus on improvements that directly enhance patient safety.
Standardized Tools and Processes
Standardized tools and workflows help reduce inconsistencies in IV line management, minimizing the risk of errors caused by varying practices across departments or shifts.
Take the Beata Clasp, for example - a tool designed to prevent line entanglement, reduce contamination, and keep IV lines off unsafe surfaces. By offering a consistent method for organizing lines, it helps staff adhere to safety protocols more effectively.
Standardized procedures for insertion, maintenance, and removal further ensure that patients receive the same level of care, no matter who is on duty. When everyone follows the same steps, reliability becomes the standard.
Staff Training and Compliance Programs
Ongoing training is key to ensuring staff consistently follow IV line safety protocols. These programs should teach both the technical skills required and the reasons behind the procedures, emphasizing how they contribute to better patient outcomes.
Training also highlights the high stakes of IV errors, as medications administered through IV lines act quickly and are absorbed directly. Compliance programs play a supporting role by monitoring staff adherence to protocols through observation, documentation reviews, and performance feedback. Regular refresher courses help address evolving challenges and reinforce essential safety practices in ever-changing healthcare environments.
How to Implement the LMAP Framework in Your Facility
Now that we've explored the importance of standardized protocols, let's look at how to put the LMAP Framework into practice. Successful implementation requires careful planning and collaboration, ensuring that every team member knows their role in maintaining IV line safety.
Step-by-Step Implementation Process
Start by forming a multidisciplinary team that includes nursing leaders, infection control experts, quality improvement staff, and frontline nurses. This group will oversee the rollout, troubleshoot challenges, and meet regularly during the early stages to keep everything on track.
Next, assess your current IV line practices. Take a close look at existing protocols, identify safety gaps, and review recent incidents involving IV lines. This initial evaluation sets the stage for tracking improvements.
From there, develop policies tailored to your facility's specific needs. Keep in mind that different units - like intensive care versus general medical floors - may require unique approaches due to varying levels of complexity and the number of IV lines per patient.
Before rolling out changes across the entire facility, pilot the new procedures in a few units. This allows you to gather feedback, identify potential workflow issues, and make adjustments as needed.
Assign champions within your facility to mentor staff and ensure compliance. These champions will play a key role in maintaining momentum after the initial training phase. Additionally, integrate standardized tools to reinforce safe IV line management practices.
Using the Beata Clasp for IV Line Organization
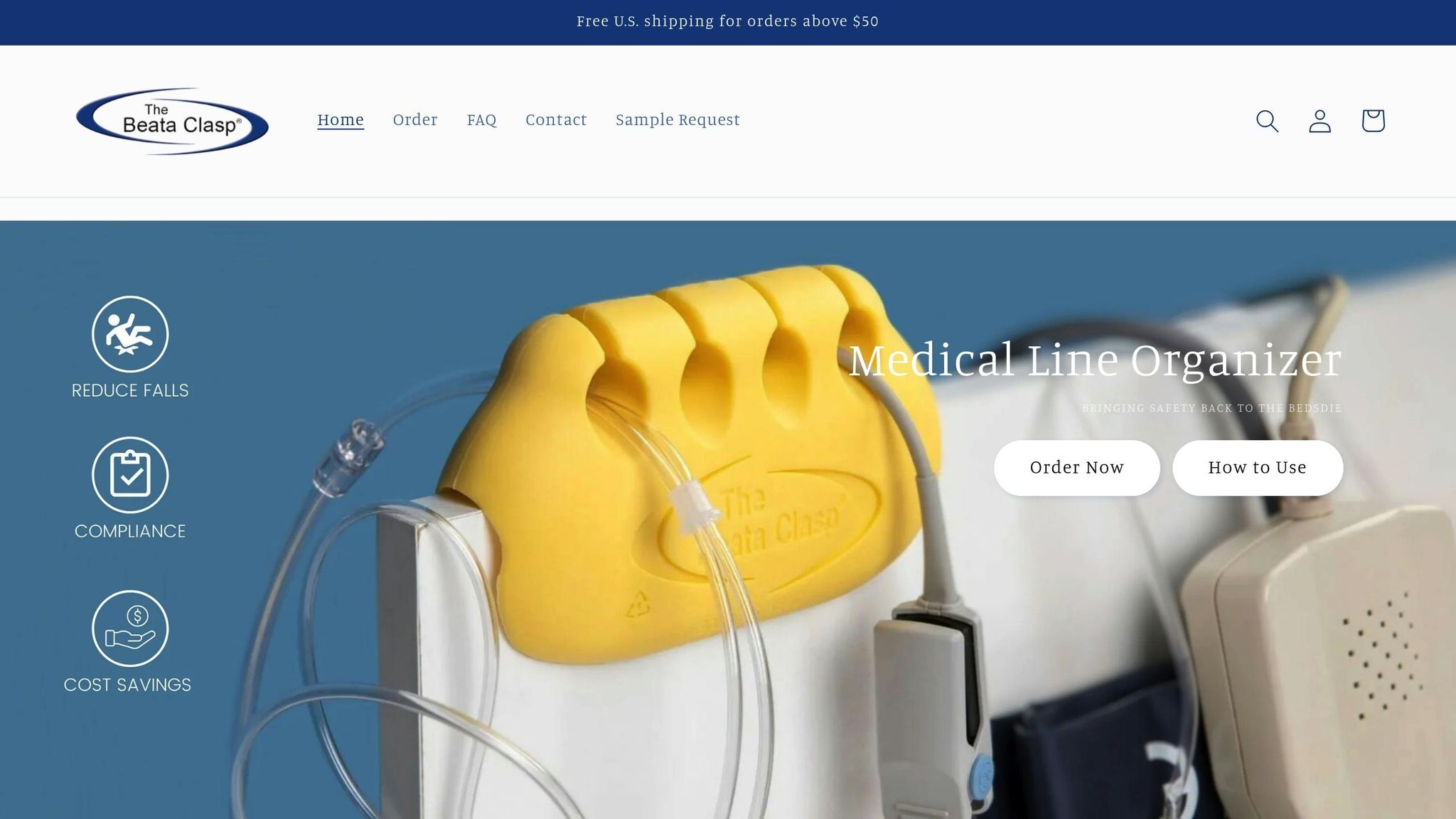
The Beata Clasp is a simple yet effective tool for organizing IV lines. Train your nursing staff on its proper use to prevent line tangling while ensuring easy access for medication administration and maintenance. Its design eliminates the need for adhesives, making it easy to reposition as patient care needs evolve.
The device’s bright, high-alert color helps it stand out, reducing the chance of oversight during patient care. To ensure a smooth integration, consider starting with evaluation packs. This allows you to test how the clasp fits into your existing workflows before committing to a larger-scale adoption.
Adapting the Framework for Different Healthcare Settings
The LMAP Framework isn’t one-size-fits-all. It can and should be adjusted to meet the unique challenges of different healthcare environments. For example:
- Critical care units often manage multiple IV lines for medications, blood products, and monitoring, making clear labeling and organization a top priority.
- Emergency departments benefit from streamlined protocols that support rapid IV line placement and quick patient transfers.
- Home healthcare may require training for family caregivers alongside professional oversight, ensuring safe and effective IV line management.
- Resource-limited facilities might explore partnerships with larger institutions or use online training modules to ensure staff education remains consistent.
Finally, establish success metrics tailored to each setting. For outpatient infusion centers, this might mean tracking complications per treatment session. Long-term care facilities could focus on infection rates and the longevity of IV lines. By customizing these benchmarks, you can better measure the framework's impact in any environment.
sbb-itb-f779e18
Risk Reduction and Patient Safety Compliance
The LMAP Framework focuses on two critical areas in healthcare: infection prevention and adherence to safety regulations. When applied correctly, this structured approach helps healthcare facilities meet essential U.S. patient safety standards while minimizing preventable risks.
Preventing Infections and Line Misconnections
Infections related to IV lines are some of the most avoidable issues in healthcare settings. The LMAP Framework tackles these risks by standardizing procedures designed to eliminate common contamination sources. For instance, keeping IV lines elevated off the floor helps prevent exposure to contaminants. The system ensures proper positioning of IV lines, keeping them clean and organized to reduce contact with potentially harmful surfaces like floors or linens.
Disorganized IV lines can also lead to dangerous misconnections, increasing the chance of medication errors during critical care. The Beata Clasp addresses this issue with its high-alert color, making it easier for healthcare providers to visually identify and trace lines in complex setups. This improved organization is especially valuable during emergencies and shift changes, saving nurses time that would otherwise be spent untangling lines. Instead, they can focus on patient care, timely medication delivery, and accurate assessments.
These measures not only improve patient outcomes but also help facilities stay compliant with strict U.S. safety regulations.
Meeting U.S. Patient Safety Requirements
Beyond infection control, the LMAP Framework aligns with mandatory U.S. safety standards. For example, the Affordable Care Act requires hospitals to implement evidence-based safety measures, a goal supported by this structured approach. By offering a systematic method for managing IV lines, the framework meets federal priorities established by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
The framework also incorporates principles from the Institute for Healthcare Improvement’s patient safety strategies, emphasizing areas like organizational culture and continuous learning. It uses clear, measurable protocols that can be evaluated through the Donabedian model, which focuses on structures, processes, and outcomes.
Additionally, the Beata Clasp contributes to compliance with fall prevention standards by minimizing trip hazards caused by IV lines and cords. This proactive approach not only protects patients and staff but also reduces the likelihood of costly incidents. By cutting down on infections, misconnections, and falls, healthcare facilities can redirect resources toward improving overall care quality and safety initiatives.
Measuring Results from the LMAP Framework
Healthcare facilities using the LMAP Framework have reported noticeable improvements in both patient safety and operational workflows. By implementing standardized protocols, staff can quickly adapt, leading to measurable advancements. These changes provide a solid foundation for assessing outcomes before and after the framework is put into practice.
Before and After Performance Metrics
Facilities have observed substantial drops in IV line-related infections, misconnections, and other safety issues. Tracking these metrics before and after implementation has shown that a structured approach to IV line management directly contributes to better patient outcomes. Considering that nearly 10% of patients in high-income countries experience an adverse event, even small improvements in these areas can make a meaningful difference in the quality of care provided.
Financial Benefits and Return on Investment
Beyond clinical improvements, the LMAP Framework offers clear financial advantages. Reduced healthcare-associated infections translate into lower costs, as these infections are tied to higher rates of illness, death, and increased medical expenses. Streamlined processes also allow healthcare teams to focus more on patient care rather than routine IV line management, cutting down on expenses linked to preventable complications.
Additionally, tools like the Beata Clasp deliver tangible value through their durability and reusability. By minimizing the need for frequent replacements of disposable line management tools, facilities can reduce supply costs and simplify operations. Adopting the LMAP Framework not only boosts patient safety but also helps healthcare institutions achieve a strong return on investment - an essential outcome in an industry where preventable harm costs billions each year.
Conclusion: Improving IV Line Safety with the LMAP Framework
The LMAP Framework provides a clear and practical approach to enhancing IV line safety. By focusing on leadership commitment, consistent monitoring, standardized procedures, and thorough staff training, it creates a reliable system that supports ongoing improvements in patient care.
Healthcare teams adopting the LMAP Framework can expect safer practices and smoother workflows that staff can trust. Its emphasis on standardization ensures that proven protocols are applied consistently, whether in a fast-paced ICU or a smaller care unit. This consistency is further strengthened by incorporating effective tools into the process.
Take, for example, the Beata Clasp - a practical tool integrated within the framework. It highlights how specific tools can significantly boost safety while aligning with the framework’s goal of achieving sustainable and cost-efficient improvements across healthcare settings.
For administrators and clinical leaders, the advantages are evident. Facilities that adopt structured protocols often see fewer infections, reduced risks of misconnections, and enhanced staff efficiency. These outcomes directly lead to better patient care and stronger operational performance.
Whether starting with a pilot program in one unit or implementing changes across an entire facility, the LMAP Framework provides the structure and guidance needed for meaningful, lasting improvements in IV line safety. Its key components - strong leadership, effective monitoring, standardized processes, and ongoing training - work together to elevate patient care and set the stage for continued success in clinical operations.
FAQs
How does the LMAP Framework help prevent infections from IV lines in healthcare facilities?
The LMAP Framework from WorldMed offers a structured approach to managing IV lines, aiming to reduce the risk of infections. It focuses on maintaining proper organization, consistent monitoring, and following patient safety standards.
This framework provides healthcare professionals with hands-on tools and clear, step-by-step strategies to ensure IV lines are managed safely throughout the facility. By prioritizing contamination prevention and enhancing safety protocols, LMAP supports a safer environment for both patients and medical staff.
How can healthcare facilities successfully implement the LMAP Framework to improve IV line safety?
To put the LMAP Framework into action, healthcare facilities should follow a clear, step-by-step plan tailored to their unique operations. Begin by thoroughly evaluating current IV line management practices. This assessment will highlight gaps and areas needing improvement, providing a solid starting point and helping to set measurable goals for enhancing safety and compliance.
Next, focus on staff training. Equip your team with the knowledge and skills they need to fully understand and implement the framework. Emphasize consistent habits, like proper labeling of lines, routine inspections, and strict adherence to infection control measures. The framework comes with ready-to-use tools and detailed strategies designed to simplify workflows and improve overall organization.
Lastly, establish a system for tracking progress. Regular audits and feedback sessions are key to identifying what’s working and what needs adjustment. Use this information to fine-tune your approach and foster a culture of ongoing improvement. By encouraging teamwork and accountability, healthcare facilities can minimize risks and ensure better safety outcomes for patients.
How can the Beata Clasp enhance IV line management for safer and more efficient healthcare practices?
The Beata Clasp offers a practical solution for improving IV line management in healthcare settings. It provides a secure and organized way to handle IV lines, helping to minimize risks like tangling, accidental disconnections, and potential contamination.
By enhancing IV line safety, this tool aligns with patient safety standards while also streamlining workflows for healthcare professionals. Its straightforward, user-friendly design makes it an effective addition to any facility's safety measures, ensuring IV lines remain secure and accessible when needed most.
