What is LMAP? Line Management Awareness Programs (LMAP) are structured approaches to improve IV line safety in healthcare. They focus on reducing errors, preventing infections, and boosting staff efficiency with standardized protocols and tools like the Beata Clasp.
Key Benefits of LMAP:
- Patient Safety: Reduces IV-related infections and medication errors.
- Staff Training: Ensures consistent safety practices through evidence-based guidelines.
- Efficient Tools: Introduces devices like the Beata Clasp to organize tubing and prevent complications.
- Cost Savings: Minimizes complications, cutting hospital stays and expenses.
Why it matters: Studies show standardized IV management can cut complications by 29%, lowering infection rates and improving patient outcomes. Tools like smart infusion pumps and incident tracking further enhance safety.
How it works: LMAP combines training, technology, and practical tools to make IV line management safer and more efficient, benefiting both patients and healthcare providers.
How To Maintain An IV Line? - Nursing Knowledge Exchange
Core Principles of Safe IV Line Management
Safe and effective IV line management is built on key principles designed to minimize complications and ensure patient safety. These guidelines serve as the foundation of any successful program, directly influencing patient outcomes in healthcare settings.
Maintaining Line Integrity
Protecting the integrity of IV lines starts with strict adherence to sterile procedures. From the moment an IV is inserted to every subsequent interaction, healthcare providers must follow aseptic techniques, including proper hand hygiene and the use of sterile equipment.
Regular site assessments are equally critical. Providers should check IV sites every four hours - or more frequently for high-risk patients - to catch early signs of infiltration, phlebitis, or infection. This proactive approach helps address issues before they escalate.
To maintain site integrity:
- Use secure devices to keep IV catheters in place and prevent accidental dislodgement.
- Flush saline locks every 8–12 hours to keep catheters clear and reduce the risk of occlusion.
- Replace administration sets according to facility protocols and immediately change any contaminated equipment.
- Manage dressings carefully to shield the insertion site from contamination. Gauze dressings should be replaced every two days, while transparent dressings can stay in place for up to seven days - unless they become soiled, damp, or loose. Promptly replacing compromised dressings helps block bacterial entry.
Of course, even the best protocols rely on skilled staff to implement them consistently. Well-trained healthcare workers are essential for maintaining these safety standards.
Staff Training and Competency
The success of IV line management also depends on the expertise of the healthcare team. Comprehensive training programs and regular competency evaluations ensure that staff are proficient in all aspects of IV care, including catheter insertion, maintenance, and infection prevention.
Only personnel with proper training should handle peripheral or central IV catheters to ensure safety protocols are followed across all shifts. Evidence-based guidelines should be the standard, with regular compliance checks to identify areas for improvement.
Staff must also be well-versed in medication compatibility, administration rates, and emergency protocols, such as the use of reversal agents. Access to up-to-date drug reference materials is vital for preventing medication errors and adverse reactions.
The data speaks volumes: up to 60% of hospital-acquired bloodstream infections are linked to vascular access devices. In facilities with fewer resources, infection rates can be three to five times higher. These statistics underscore the importance of following these principles - not just as a matter of best practice, but as a critical factor in patient safety and recovery.
Healthcare facilities that prioritize staff training see measurable gains in safety outcomes. When teams consistently apply these core principles, they create a safer environment for IV therapy, benefiting both patients and providers alike.
Practical Strategies for Organizing and Monitoring IV Lines
Managing IV lines effectively requires more than just following safety protocols - it calls for a structured approach to organization and monitoring. When healthcare facilities adopt systematic strategies, they often see better patient outcomes and improved staff efficiency.
Methods for Organizing IV Lines
Keeping IV lines organized is crucial for patient safety. Start by tracing each tube from the patient to its source to confirm the correct port is in use. To further reduce risks, consider using sutureless securement devices. These tools not only keep lines well-organized but also help prevent accidental dislodgement, making it easier to identify and manage each line.
Best Practices for Monitoring IV Lines
Once the lines are properly set up, continuous monitoring is essential to catch potential complications early. Regular checks of the IV site can help detect warning signs like redness, swelling, or tenderness. When starting new fluids or medications, confirm the IV site’s patency by aspirating for blood return and flushing the catheter as per protocol.
Advancements in technology, like smart infusion pumps and in-line pressure monitoring (ILPM), offer additional safeguards. These tools can identify early signs of issues such as infiltration, extravasation, or occlusions by monitoring pressure changes in the IV lines.
For example, a study conducted at Frimley Health NHS Foundation Trust tracked 2,254 IVs over 3,507 hours using ivWatch's SmartTouch sensor. The system issued 122 red Check IV notifications, helping to prevent injuries in 5.4% of infusion activities. Nurses participating in the study reported greater confidence in monitoring and felt that the technology enhanced patient safety perceptions.
Patient education also plays a key role. Encouraging patients to report any discomfort or changes at the IV site can lead to quicker interventions. Additionally, using incident reporting systems provides valuable data for improving care quality. Research shows that patients with IV complications tend to stay in the hospital for an average of six days, compared to four days for those without, leading to higher healthcare costs.
Using the Beata Clasp for Line Management
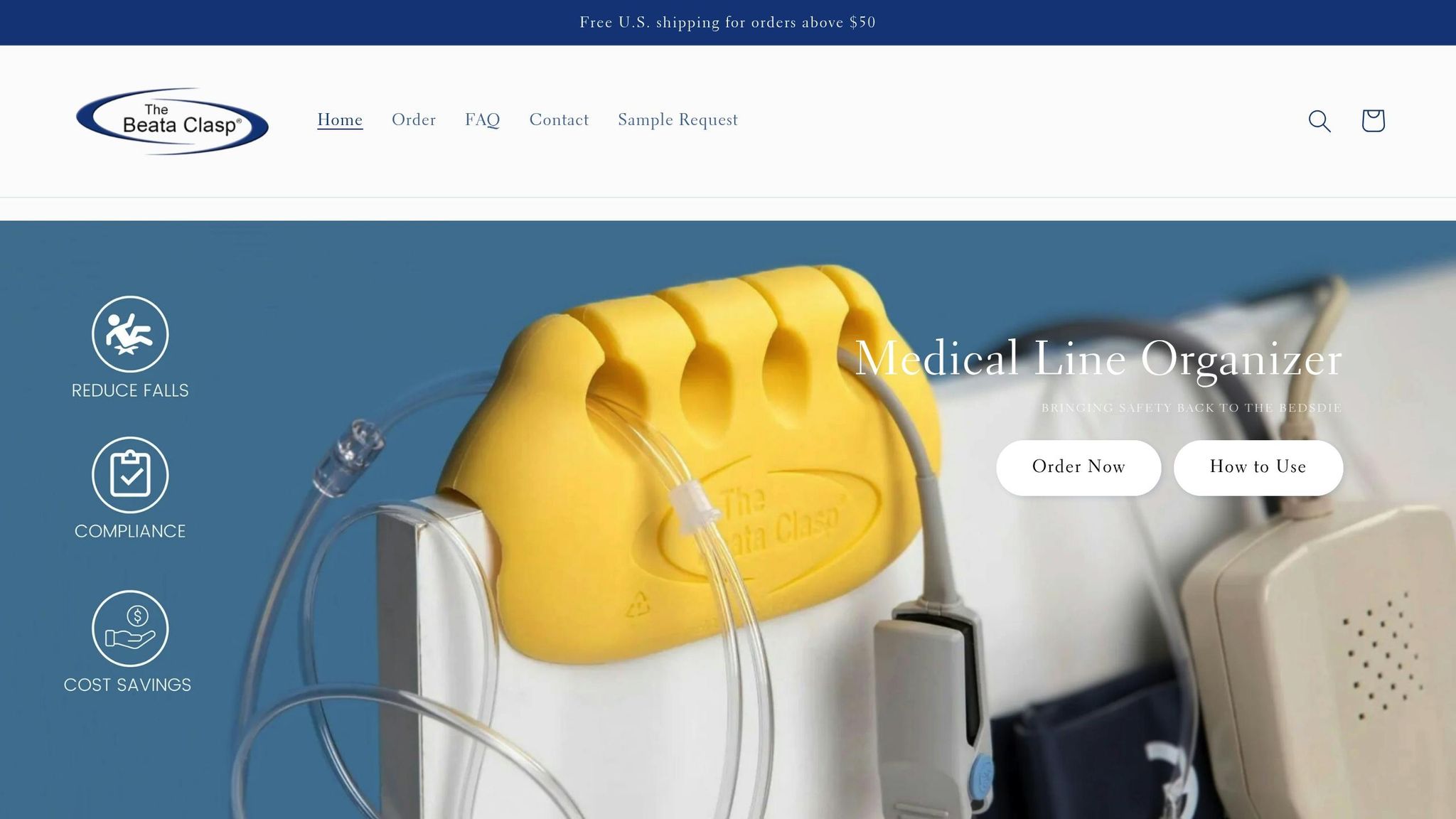
Specialized tools, like the Beata Clasp, add another layer of efficiency to IV line management. This device builds on existing organizational and monitoring practices by offering targeted solutions. Its antimicrobial properties help reduce the risk of healthcare-associated infections, which remain one of the top 10 causes of death in the U.S.. The clasp’s high-alert color makes it easier for staff to quickly identify and assess IV lines.
Designed with practicality in mind, the Beata Clasp features an easy-to-clean, latex-free design that minimizes allergy risks. It also helps prevent tangling and accidental disconnections, simplifying the process of tracing IV lines from the patient to the source. With options for both single-patient and multi-patient use, the device supports various clinical protocols and infection control measures, making it a versatile addition to healthcare settings.
sbb-itb-f779e18
Tools and Technologies for IV Line Safety
The world of healthcare technology offers a range of solutions to tackle challenges in IV line management. With nearly 40% of medical errors happening during medication administration and about one in 20 hospital patients experiencing an adverse drug event, the need for effective tools has never been more pressing.
Some of the most impactful tools include smart infusion pumps equipped with pressure sensors and incident reporting software for real-time tracking. These technologies are designed to streamline workflows while improving patient outcomes.
Features and Benefits of IV Line Management Tools
When selecting IV line management tools, healthcare facilities should prioritize features that address the root causes of IV-related complications while enhancing workflow efficiency. The most effective tools combine patient safety benefits with practical workflow improvements.
| Feature | Patient Safety Benefit | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Antimicrobial Properties | Reduces risk of healthcare-associated infections | Lowers frequency of line replacements |
| Line Organization | Prevents misconnections and medication errors | Saves time during patient assessments |
| Visual Identification | Simplifies line tracing and verification | Eases transitions during shift changes |
| Secure Attachment | Prevents accidental disconnections | Reduces rework and patient discomfort |
| Easy Cleaning | Helps maintain infection control standards | Speeds up room turnover |
Products like the Beata Clasp incorporate these features, addressing clinical challenges head-on.
Patients with IV-related complications face average hospital bills of $11,000 compared to $7,000 for those without complications. Tools that help prevent these issues can make a meaningful difference in both patient care and healthcare costs.
Adding Tools to Daily Practice
Integrating these tools into daily workflows can significantly improve patient safety when paired with strong organization and monitoring practices. Facilities should start by identifying common IV-related issues. For example, IV failure rates can reach 53%, and infiltration occurs in over 16% of cases. By addressing these specific challenges, healthcare providers can better measure the impact of new tools on patient outcomes.
The Beata Clasp offers practical solutions by reducing tangling, saving time at the bedside, minimizing frustration, and decreasing rework. It also helps keep call lights within reach, reduces contamination, and prevents lines from touching the floor, all while minimizing misconnections and avoiding trips and falls.
What’s more, the Beata Clasp requires little to no staff training, as it organizes tubing without the need for in-service sessions. Its adhesive-free and recyclable design aligns with sustainability goals and infection control protocols. Plus, its versatility for both single-patient and multi-patient use supports consistent safety practices, making it a valuable tool for nurse-led safety initiatives and LMAP implementation.
Nurse-Led Programs and Best Practices
Nurse-led initiatives are at the forefront of improving patient safety, transforming standardized protocols and advanced tools into practical, everyday solutions. By leveraging their hands-on experience, nurses play a key role in enhancing IV line management and identifying strategies that make a real difference in patient care.
Nurse-Led Workflow Improvements
Nurses bring practical, actionable ideas to streamline IV line management. These initiatives often focus on standardizing procedures, improving team communication, and implementing systems to reduce errors. A great example comes from a hospital in Qingdao, where the VAST program significantly improved catheterization success rates and compliance with central line management protocols. The program included on-the-job training, an emergency "green channel" for urgent cases, standardized clinical rounding, and clear self-care instructions for patients.
To keep these improvements on track, ongoing audits help identify where protocols need adjustment. For instance, one quality improvement project utilized targeted education tools and regular audits, achieving a standardized infection ratio between 0.787 and 3.343 from January 2020 to September 2021. Notably, higher ratios were linked to increased patient numbers during the COVID-19 pandemic, highlighting the importance of adaptable workflows. These efforts contribute to a stronger foundation for a culture of safety.
Building a Culture of Safety
A lasting culture of safety thrives on open communication, continuous learning, and proactive risk management. Nurses play a crucial role in fostering this environment through peer education, constructive feedback, and clear communication during critical transitions like shift changes.
The need for such a culture is evident in key statistics: approximately 30% of IV medication administrations involve errors, with 10% of these errors being IV-specific. Additionally, 57.9% of IV infusion errors are linked to incorrect administration rates. Collaborative rounding teams, often led by clinical nurse specialists, have proven effective in raising awareness of prevention strategies and reinforcing a safety-first mindset.
Empowering patients is another cornerstone of safety. Providing detailed educational materials and pre-treatment briefings enables patients to take an active role in their own care, enhancing overall safety.
Sustaining these improvements requires addressing the challenges of workload and burnout. Nurses who advocate for flexible scheduling, wellness programs, and adequate staffing help ensure that safety protocols are consistently followed. Regular feedback mechanisms, such as incident report reviews and trend analyses, allow safety measures to adapt and stay effective over time.
Conclusion
Line Management Awareness Programs (LMAPs) mark a shift from simply acknowledging IV line management challenges to actively addressing them in healthcare settings. By adopting a structured approach, these programs directly contribute to patient safety through the use of standardized protocols, evidence-based practices, and practical tools.
This guide outlines strategies that can lead to real improvements in patient care. Standardizing IV line management processes across facilities helps ensure consistency and reduces variations in care. At the same time, regular staff training and ongoing competency checks help maintain high standards and encourage a collective commitment to safety.
Innovative tools, like the Beata Clasp, simplify IV line management, reduce infection risks, and streamline workflows. Incorporating such tools into everyday practice shows how physical systems can improve both safety and efficiency in clinical environments.
The success of LMAPs relies on a cohesive approach that includes digital tools, strong leadership, and continuous performance evaluation. Tracking key metrics provides clear evidence of the program’s impact, ensuring that improvements are measurable and sustainable.
FAQs
How does Beata Clasp help reduce IV-related infections in healthcare environments?
Beata Clasp is a game-changer in reducing IV-related infections by keeping tubing organized and secure, which helps prevent accidental contamination. Its thoughtful design cuts down on unnecessary handling of IV lines and safeguards access points with antimicrobial protections, reducing the chances of microbial entry.
By simplifying line management, Beata Clasp boosts patient safety and helps healthcare professionals maintain cleaner, more efficient workflows - making a real difference in patient care.
How do smart infusion pumps and in-line pressure monitoring improve patient safety during IV therapy?
Smart infusion pumps and in-line pressure monitoring are essential tools in IV therapy, designed to enhance patient safety and ensure accurate medication delivery. These devices use advanced alert systems to quickly identify potential problems, such as blockages or unusual pressure changes, allowing healthcare providers to address issues before they escalate.
With precise control over drug dosages and instant feedback on system performance, these technologies help reduce complications, lower the risk of infections, and improve overall patient care. Their seamless integration into IV therapy processes not only boosts safety but also streamlines the workflow for medical teams.
How can healthcare facilities implement Line Management Awareness Programs (LMAP) to enhance patient safety and staff efficiency?
Healthcare facilities can make Line Management Awareness Programs (LMAP) work effectively by emphasizing clear workflows and actively involving staff. Tools like process mapping are a great starting point to spot inefficiencies and identify safety risks in IV therapy and line management. This approach not only helps organize tasks but also reduces the likelihood of errors.
Equally important is promoting open communication and teamwork among staff members. A collaborative environment leads to better decision-making, minimizes mistakes, and ensures consistent care for patients. By combining these efforts into a comprehensive safety program, healthcare teams can deliver better patient outcomes while improving day-to-day operations.
